Understanding Patient Safety Indicators: Measuring What Matters

Every year, preventable medical errors affect thousands of patients—underscoring the critical need for tools like Patient Safety Indicators (PSIs) to measure and improve care. In fact, one study highlighted by the National Library of Medicine revealed that approximately 400,000 hospitalized patients experience preventable harm annually, with over 200,000 deaths attributed to avoidable medical errors, highlighting the urgent need for effective monitoring and intervention strategies.
Patient Safety Indicators (PSIs) are standardized measures that assess the quality and safety of care delivered in hospitals and healthcare facilities. Developed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), PSIs are designed to identify potential adverse events and preventable complications, such as infections, surgical errors, or injuries, that may occur during a patient’s hospital stay. A lower rate indicates better hospital performance, meaning fewer medical errors or adverse events. By highlighting areas where safety lapses occur, PSIs serve as valuable tools for improving healthcare systems, protecting patient outcomes, and reducing healthcare costs.
Their introduction in the early 2000s marked a transformative step in healthcare research, enabling hospitals and policymakers to monitor adverse event rates and work toward safer, more efficient care. These indicators not only foster quality improvement but also influence hospital accreditation, overall health system improvement, and compliance with regulatory standards.

Nationally Recognized Quality Indicators
Patient Safety Indicators (PSIs) focus on critical areas of healthcare where preventable harm can occur, providing a standardized way to evaluate safety and identify opportunities for improvement. The AHRQ PSIs indicators span various aspects of patient care, from surgical outcomes to obstetric trauma to infection prevention. Below are some of the most critical PSIs, each representing a significant aspect of hospital performance and safety:
PSI 02: Death Rate in Low-Mortality Diagnosis-Related Groups (DRGs) tracks deaths among patients with conditions where mortality is expected to be minimal, revealing areas where care delivery may fall short.
PSI 03: Pressure Ulcer Rate measures the occurrence of preventable pressure ulcers, indicating gaps in nursing care or patient monitoring.
PSI 04: Death Rate Among Surgical Inpatients with Serious Treatable Complications evaluates hospitals’ effectiveness in managing critical complications, such as pneumonia or sepsis, in surgical patients.
PSI 08: In-Hospital Fall-Associated Fracture Rate highlights patient falls resulting in fractures, underscoring the importance of fall prevention protocols.
PSI 13: Postoperative Sepsis Rate tracks severe infections that occur after surgery, which are often preventable through proper sterile techniques and timely intervention.
PSI 17: Birth Trauma Rate – Injury to Neonate tracks injuries sustained by newborns during vaginal delivery, reflecting the quality of perinatal care.
By regularly monitoring these indicators, healthcare providers can target quality improvement efforts, reduce preventable harm, and improve patient outcomes, while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and benchmarking performance against the best hospitals nationally.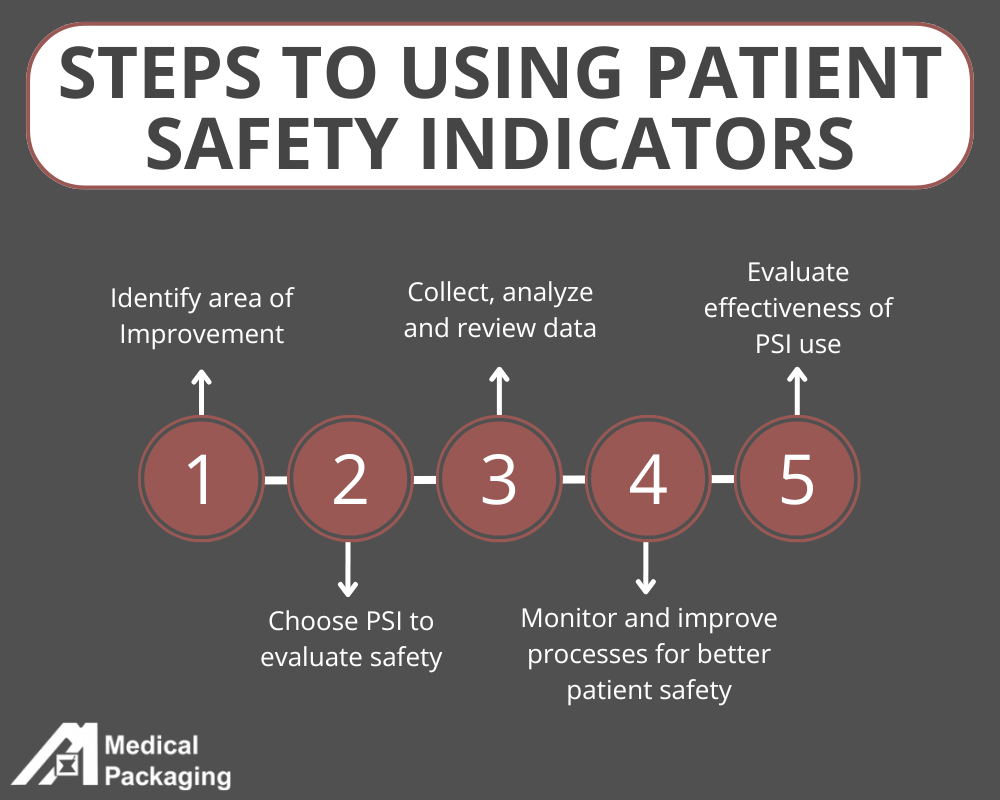
Selecting the Appropriate Patient Safety Indicators
Choosing the appropriate Patient Safety Indicator (PSI) to evaluate your organization is a critical step in driving meaningful improvements in care quality and safety. The selection process should align with your organization’s goals, patient population, and areas of high-risk care. Start by identifying key priorities, such as reducing adverse event rates, improving outcomes in specific departments (e.g., surgery or maternal care), or addressing regulatory compliance. Ensure the area is specific and data can be collected over time to develop accurate insights. Keep in mind what records and resources (such as electronic health records) your organization has in place to collect and analyze data.
When applicable, use the nationally recognized AHRQ PSIs in order to compare data across healthcare facilities. PSIs are also valuable tools for peer-to-peer comparison, allowing organizations to benchmark their performance against similar facilities at the national level or within their network. This fosters transparency, highlights areas of excellence, and identifies opportunities for growth. Additionally, ensure the selected PSI aligns with available data and resources for accurate tracking and analysis. Ultimately, selecting the right indicator allows your organization to target improvement efforts effectively, benchmark performance, and demonstrate a commitment to deliver safer, higher-quality care. 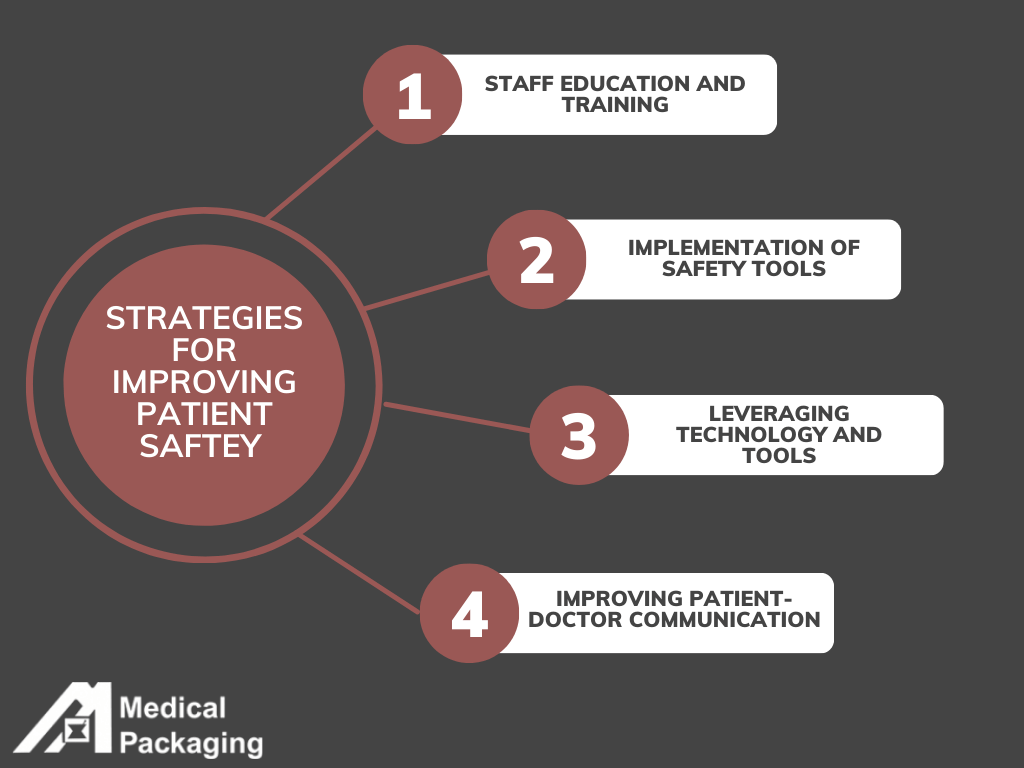
Implementing Patient Safety Indicators
Implementing Patient Safety Indicator (PSI) scores requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both systemic processes and specific areas of care. By focusing on prevention, education, and innovation, healthcare providers can reduce adverse event rates and enhance patient safety performance. Periodically, it is important to reassess past trends, future goals and adjust PSIs as needed. Below are key strategies to consider:
1. Staff Education and Training
Equipping healthcare providers with the knowledge and skills to follow evidence-based safety practices is fundamental. Regular training in infection control, surgical protocols, and fall prevention ensures that staff remain proactive in minimizing risks.
2. Implementation of Safety Protocols
Standardized protocols for high-risk areas, such as surgical procedures or catheter insertions, help reduce variability and prevent errors. Protocols should also include systems for identifying and addressing potential complications, such as pressure ulcers or postoperative sepsis, early.
3. Leveraging Technology and Tools
Advanced technologies, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and clinical decision support systems, play a crucial role in tracking patient safety events and ensuring compliance with safety protocols. Additionally, smart medical packaging with features like clear labeling, tamper-evident seals, and traceability systems reduces medication errors and supports overall safety efforts.
4. Improved Communication and Collaboration
Open lines of communication between healthcare teams, patients, and families are essential for improving outcomes. Collaborative approaches to care, such as daily safety huddles and patient education, help prevent miscommunication that could lead to errors in individual cases.
Improving Patient Safety Through PSIs
Monitoring PSIs is a vital practice for ensuring high-quality healthcare and reducing preventable harm in healthcare settings. By analyzing PSI data, healthcare providers can identify similar patterns, address systemic gaps, and implement targeted interventions to improve outcomes. Smart tools, such as tamper-evident medical packaging with clear labeling and traceability features, play a significant role in preventing medication errors and ensuring patient safety. Additionally, fostering open communication between healthcare teams and patients promotes collaboration and reduces the risk of miscommunication, which is often a factor in patient safety incidents.
While PSIs are not required, they have broader implications for hospital accreditation, compliance with safety standards, and public trust. Metrics like the PSI 90 Composite allow facilities to benchmark their performance against others at the national level, fostering transparency and driving quality improvement efforts. Furthermore, accurate monitoring helps reduce healthcare costs by preventing complications that lead to extended hospital stays or costly interventions. By embedding PSI tracking into daily operations, healthcare systems not only protect patients but also ensure they meet regulatory requirements and maintain their reputation as leaders in safety and care excellence.
The Role Medical Packaging Plays in Patient Safety
Medical packaging is a crucial component in ensuring patient safety. Well-designed and implemented packaging systems directly reduce the risk of medication errors, contamination, and product misuse—factors that significantly impact Patient Safety Indicators (PSIs). By providing clear labeling, tamper-evident seals, and traceability features, medical packaging helps healthcare providers quickly and confidently identify medications and devices, minimizing the chances of human error.
Error Prevention Through Packaging
Medical packaging acts as a frontline defense against errors in fast-paced healthcare environments. Clear identification systems ensure that medications and medical devices are accurately administered, while tamper-evident features guarantee the integrity of the product, preventing contamination or misuse. Furthermore, high-quality packaging helps maintain the stability of sensitive items, ensuring they remain effective throughout their intended use. For example, PSI 13: Postoperative Sepsis Rate, which tracks the occurrence of severe infections following surgical procedures. Proper medical packaging plays a pivotal role in preventing infections by ensuring the sterility and integrity of medical devices, surgical tools, and medications.
Meeting Safety Standards
Adherence to regulatory standards and industry best practices is critical for hospitals and healthcare facilities, aiming to improve their patient safety performance. Advanced medical packaging solutions not only meet these standards but also exceed them by integrating innovative features that promote safety, compliance, and efficiency. Packaging that aligns with quality assurance measures ensures healthcare providers can deliver care with confidence, avoiding errors that could impact adverse event rates or hospital performance on PSIs.
Best Practices with Medical Packaging
To maximize the impact of medical packaging on hospital safety, healthcare facilities should prioritize solutions that include sterile barrier systems, clear labeling and instructions, tamper-evident designs, and traceability features. These elements work together to prevent errors, support compliance, and improve patient outcomes by providing healthcare providers with the tools they need to deliver safe and effective care.
By leveraging high-quality medical packaging solutions, such as those offered by Medical Packaging Inc., LLC (MPI), hospitals and healthcare facilities can enhance their quality improvement initiatives, reduce preventable harm, and improve performance on key PSIs. Proper packaging is more than a logistical necessity, it is an integral part of creating a safer and more reliable healthcare system.
The Path to Safer Healthcare Starts Here
Every aspect of the healthcare process contributes to patient safety, and Patient Safety Indicators (PSIs) provide a critical framework for identifying and addressing preventable harm. From monitoring key metrics like pressure ulcers and postoperative sepsis to implementing strategies such as staff training, safety protocols, and advanced technology, improving PSI scores requires a comprehensive, organization-wide commitment. While often overlooked, medical packaging plays a vital role in this effort, ensuring the integrity, sterility, and accurate labeling of medications and devices—critical elements in reducing errors and improving patient outcomes.
By partnering with MPI, healthcare facilities can strengthen their safety initiatives and achieve measurable improvements in their PSI performance. MPI’s high-quality packaging solutions are designed to meet the strictest safety standards, helping hospitals and healthcare systems prevent errors, ensure compliance, and deliver safer care. Take the next step in enhancing patient safety—explore how MPI can support your facility today.
Contact MPI Today for Personal Assistance
MPI’s Drug Master File provides speed-to-market regulatory and technical support related to our packaging components for medical and pharmaceutical market clients