Prepackaged Medication Dispensing: The Future of Pharmacy

Prepackaged medication dispensing is transforming the pharmacy landscape in the United States. As health systems prioritize patient safety, medication adherence, and operational efficiency, unit dose solutions are helping healthcare providers improve outcomes while reducing medication errors and adverse events.
The Unit Dose Supply Method
Many prepackaged medication systems are built on the unit dose supply method. Designed to provide patients with the exact recommended dosage of prescription medication, the unit dose method helps maximize all benefits the repackaging process provides to healthcare markets.
A unit dose packaging system can dispense various medication forms including tablets, capsules, injectables, and liquids. Unit dosages can also develop patient-specific treatments incorporating multiple medications. Each package receives proper labeling for identification until patient administration. The packaging includes detailed information such as the drug’s generic name, strength, control number, and expiration date, minimizing contamination caused by transfer and handling.
Unit dose prepackaged medications reduce medication error risk and improve medication adherence. Controlled substances, prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and emergency medications can all be prepackaged for efficient dispensing.
Physician Dispensing
Prepackaged medication dispensing is becoming increasingly beneficial in physicians’ offices and clinics across the United States. Using prepackaged medications to support in-office dispensing programs enables dispensing practitioners, including physicians and physician assistants, to supply single-dose, prepackaged medication directly to their patients.
Although most state laws permit healthcare providers to purchase and dispense medications directly from their clinics, the dispensing process is highly regulated by each state under federal law. A dispensing physician must meet specific registration requirements and follow federal regulations governing dangerous drugs and controlled substances under the Controlled Substances Act.
As an additional service, medical practitioners interested in in-house dispensing typically partner with a repackaging company. These wholesale distributors handle the entire repackaging and labeling process while following strict FDA and cGMP guidelines, ensuring compliance with reporting requirements.
Prepackaged Medications in Institutional Pharmacies
Hospital pharmacies and outpatient pharmacies, including those operating in critical access hospitals or long-term care facilities, tend to experience the repackaging and prepackaged medication process on a larger scale. With more resources and in-house capabilities, these health systems might establish an internal prepackaged dispensing program. The facility first determines which medications are best suited for the unit dose supply method and plans a system around the equipment, materials, and strategy needed to produce prepackaged medications for patients.
Smaller organizations or those unable to allocate necessary resources will outsource the program, relying on a repackager to provide medications in unit dose packages while maintaining compliance with federal regulations.
The convenience offered by prepackaged medication dispensing benefits every patient but proves especially helpful for administering prescription drugs to those with complicated dosing regimens. This includes seniors and at-risk patients. With only the proper dosage, these patients better understand how many pills and when to administer their prescription medication, reducing accidental overdose risk and increasing medication adherence likelihood. Beyond the patients themselves, prepackaged medication also benefits nurses and caregivers who might be responsible for managing their patients’ or loved ones’ medication regimens.
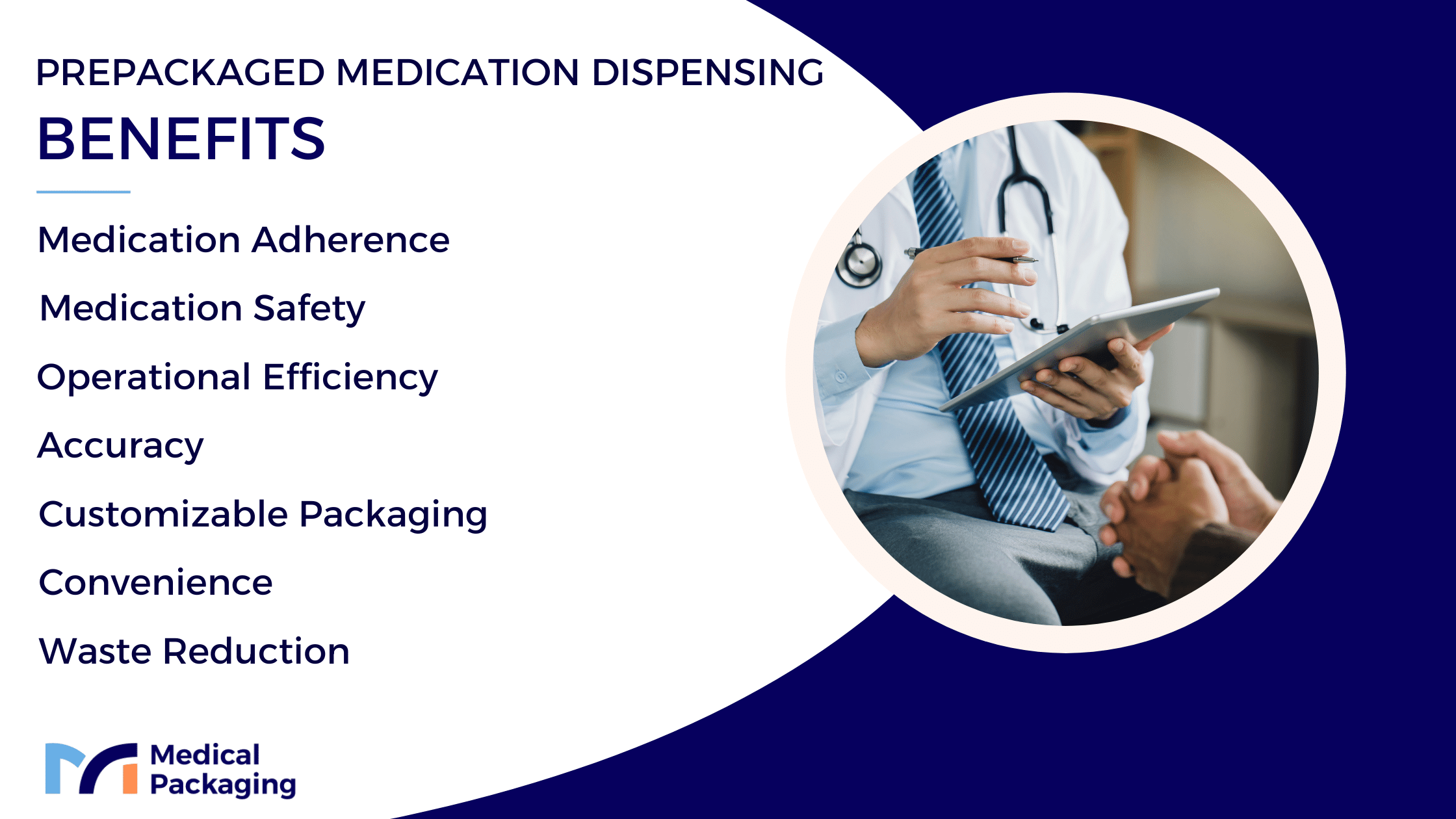
The Benefits of Prepackaged Medication Dispensing
As mentioned, patient safety and medication adherence are major benefits that prepackaged dispensing brings to both traditional pharmacy operations and medical facilities. Beyond these factors, the dispensing process delivers various other advantages benefiting healthcare providers and patients, following best practices in medication management.
Improved Accuracy
Automated labeling and barcoding systems help pharmacists and other healthcare providers reduce medication error rates. Traceability supports compliance with reporting requirements and helps prevent the distribution of expired medications.
Reduced Waste
Prepackaged dispensing supplies only the necessary dosage, reducing leftover medication, limiting disposal of dangerous drugs, and lowering costs related to expired or unused inventory.
Operational Efficiency
By streamlining the dispensing process, healthcare organizations spend less time coordinating prescriptions. It frees up resources for better patient care and faster treatment turnaround.
Increased Convenience
Prepackaged medications allow healthcare providers to offer one-stop care—from diagnosis to prescription—improving patient satisfaction and adherence. This model also supports effective patient counseling and clear prescription order handling.
Revenue Opportunity
For dispensing practitioners in clinics and smaller offices, offering in-house medication can generate new revenue streams while strengthening the patient-provider relationship.

Female doctor is treating a patient and dispensing medicine.
Key Challenges in Physician Dispensing
Before incorporating in-house dispensing in their business model, physicians should consider key challenges throughout the process.
Regulations & Laws
As mentioned, physician dispensing is highly regulated by each state under federal law. Healthcare providers face multiple regulatory requirements:
- State-specific limitations and rules governing dispensing authority
- Quantity restrictions and labeling requirements that vary by jurisdiction
- Controlled Substances Act requirements for controlled substance dispensing
- Additional registration and licensing costs
- Proper prescription blank maintenance and written prescription requirements
- Federal regulation compliance as mandated by regulatory agencies
Administrative Burden
Key decisions must be made throughout the process, but with adequate administrative capacity, organizations should be able to outline and address each concern. Major administrative challenges include:
- Serving patients with different insurance coverage requirements
- Stocking specific drugs covered by various providers
- Meeting patient counseling requirements and maintaining proper documentation
- Managing the complexity of generic drug focused programs to reduce administrative load
Key Challenges in Institutional Prepackaged Dispensing
Budget Considerations for Implementation
Whether an organization plans on repackaging and labeling internally or outsourcing prepackaged efforts, the administration team must budget for the new service. Financial considerations include:
- Additional costs to meet federal regulations and compliance requirements
- Program enrollment fees for prepackaged dispensing services
- Equipment and supply costs for in-house operations
- Disease control and safety protocol implementation expenses
Before deciding which route to take, it is crucial to map out each scenario and incorporate extra costs into your budget.
Workflow Integration and Impact Assessment
It is important to assess the impact prepackaging will have on staff and patient care workflow. Organizations must consider:
- Varied effects across different departments and patient populations
- Specific requirements for pediatric wards versus adult care areas like critical access hospitals
- Clinical trial operations with specialized medication packaging and tracking needs
- Professional practice standards compliance across different care markets
- Equipment and supply variations needed for different medication forms
Equipment and Partnership Selection
If an organization is taking the repackaging process in-house, they need to identify the right equipment and partnerships. Key selection criteria include:
- Productivity and profitability optimization for unit dose supply implementation
- Federal government regulation compliance capabilities
- Proper documentation and reporting systems
- Regulatory agency requirement adherence
- Integration with existing pharmacy systems and workflows
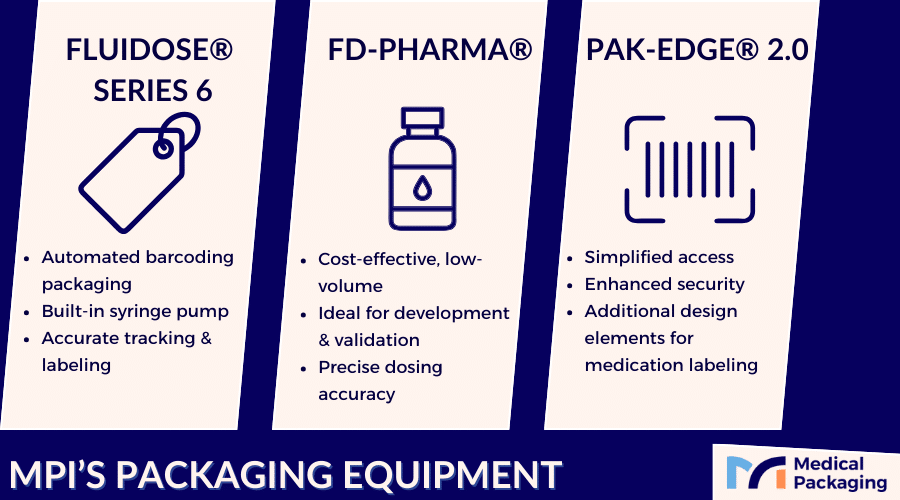
Medical Packaging Inc., LLC (MPI)'s Unit Dose Supply Solutions
Medical Packaging Inc., LLC (MPI) supports health systems, hospitals, and wholesale distributors with pharmaceutical packaging equipment and labeling software that meet federal regulations. Their solutions support compliance, improve accuracy, and enhance operational performance across healthcare markets.
MPI’s Pharmaceutical Packaging Equipment
Fluidose® Series 6
Automated barcoding packaging system for unit dose oral medications with built-in syringe pump mechanism. Integrates with existing pharmacy systems while maintaining accurate expiration date tracking.
FD-Pharma®
Delivers precise liquid medication doses into high-quality unit dose cups. FDA-compliant solution ideal for low-volume production, clinical trials, and specialty applications.
Pak-EDGE® UD Barcode Labeling Software 2.0
Advanced labeling program with enhanced security options for controlled substance management. Provides patient identification, prescription order details, and dispensing practitioner information to reduce medical errors and ensure federal regulation compliance.
Content
- The Unit Dose Supply Method
- Physician Dispensing
- Prepackaged Medications in Institutional Pharmacies
- The Benefits of Prepackaged Medication Dispensing
- Key Challenges in Physician Dispensing
- Key Challenges in Institutional Prepackaged Dispensing
- Medical Packaging Inc., LLC (MPI)'s Unit Dose Supply Solutions
Contact MPI Today for Personal Assistance
MPI’s Drug Master File provides speed-to-market regulatory and technical support related to our packaging components for medical and pharmaceutical market clients